11
2023
-
09
From bronze to king, the road of advancement for scientific researchers (2) - Tutorial on the basic operation of cellular experiments
Cell culture is the most basic operation for cell experiments. Through cell culture, we can obtain a large number of cells, which can be used for further research on cell function and signalling pathways, so the quality of cell culture will directly affect the subsequent cell experiments and the accuracy of the results.

01 cell culture
Cell culture is the most basic operation for cell experiments. Through cell culture, we can obtain a large number of cells, which can be used for further research on cell function and signalling pathways, so the quality of cell culture will directly affect the subsequent cell experiments and the accuracy of the results.
Cells are very fragile and need to be taken care of like children in the process of cell culture, and their status needs to be observed every day in order to adjust the culture system or to be handled accordingly. As the growth characteristics of each type of cell are different, it is important not to operate mechanically and dogmatically.
As the cell culture medium contains a large number of nutrients, ubiquitous microorganisms may reproduce in it, once the cell culture medium is contaminated, it will spread rapidly, thus affecting the quality of cell growth, so the whole process of cell culture should follow the principle of aseptic operation.
Commonly used reagents and their functions

▲Basal medium (copyrighted image, please do not reproduce)
Basic medium: mainly composed of amino acids, vitamins, carbohydrates, inorganic ions, etc. It provides the basic nutrients and culture environment (pH, CO2 concentration) required for cell growth. Common basic culture media include: MEM, DMEM, RPMI-1640, F-12, etc. Different culture media are suitable for different cell lines.

▲Fetal bovine serum (copyrighted image, please do not reproduce)
Fetal bovine serum: It is a widely used additive in cell culture, which is taken from calf foetus delivered by caesarean section, and contains various growth factors, peptides, hormones, binding proteins, etc. It provides various nutrients necessary for cell growth, and 10% concentration of fetal bovine serum is used in general cell culture medium, and the concentration required by different cells is different.

▲Dual Resistance (copyrighted image, please do not reproduce)
Double antibiotic: It is the most commonly used antibiotic in cell culture, the components are penicillin and streptomycin, penicillin has the effect of killing Gram-positive bacteria, streptomycin mainly works with Gram-negative bacteria, it is often added to the cell culture medium at 1% concentration to prevent cell contamination during cell culture.

▲PBS (copyrighted image, please do not reproduce)
PBS: i.e. phosphate buffer solution, is the most commonly used buffer salt solution in cell culture, composed of disodium hydrogen phosphate, sodium chloride, potassium dihydrogen alternatively, potassium chloride, isotonic with human blood, commonly used in cell washing and reagent configuration.

▲Trypsin (copyrighted image, please do not reproduce)
Trypsin: a protein secreted by the pancreas, commonly used in the digestion of adherent cells and the dispersion of tissue cells, often adding EDTA to increase the digestive effect, its digestive activity can be inhibited by serum.
Commonly used instruments and their functions
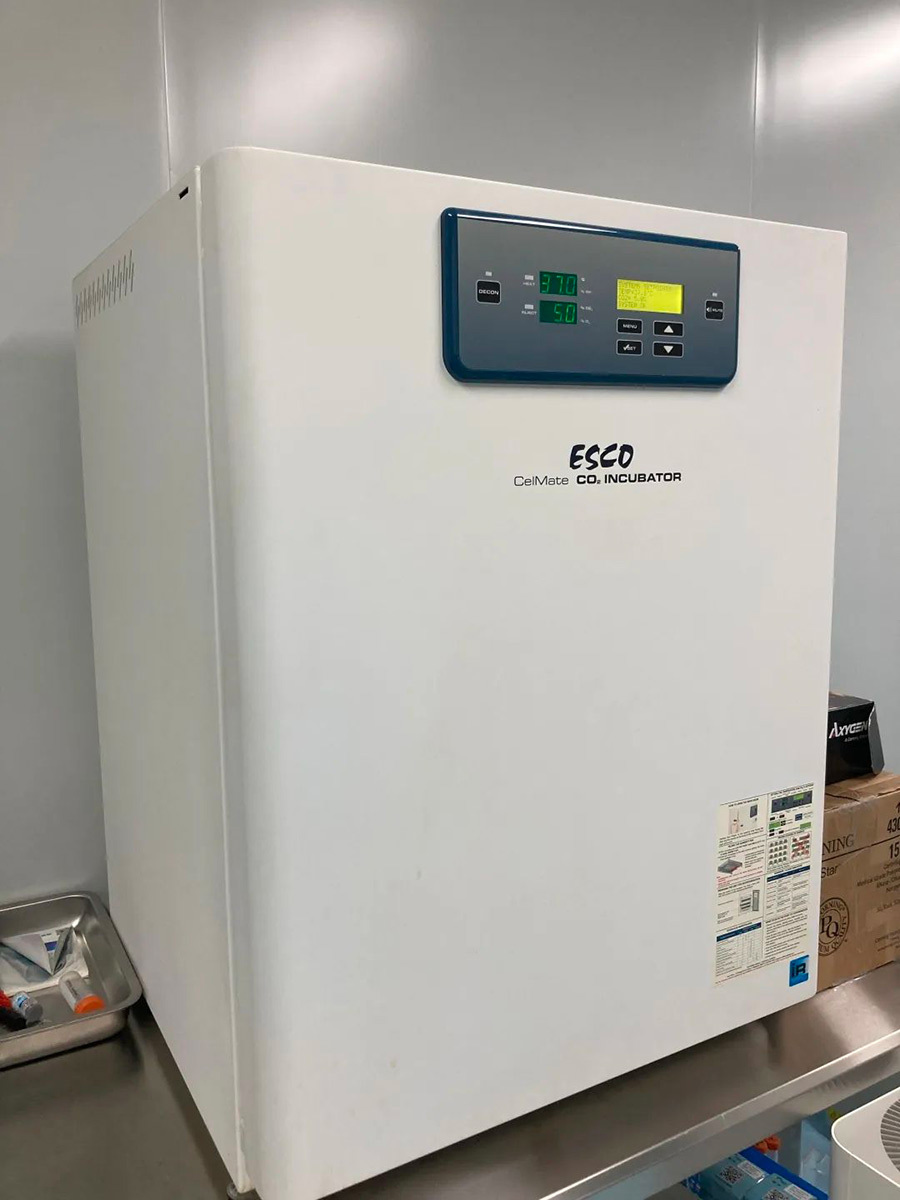

▲Cell culture incubator (copyrighted image, please do not reproduce)
Cell culture incubator: It is the most central equipment in the cell culture process, providing a comfortable environment for cell growth. The culture conditions for most cells are 37℃, 5% CO2 concentration and certain humidity.
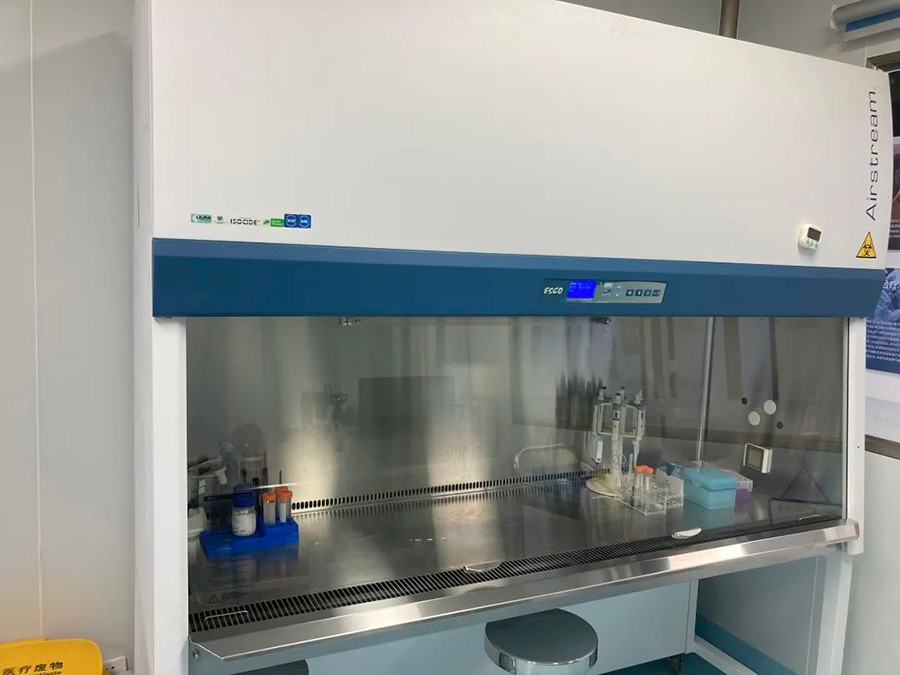

▲Clean bench/biosafety cabinet (copyrighted image, please do not reproduce)
Ultra-clean bench/biosafety cabinet: It is the main equipment for cell experimental operation, which can provide a dust-free, sterile and high-clean operation environment. Ultra-clean bench can protect cell samples, and biological safety cabinet can protect both cell samples and operators.
▲Inverted microscope (copyrighted image, please do not reproduce)
Inverted microscope: used to observe the growth state of cells in the culture vessel, microscopes with fluorescence modules can also be used for the observation of cell fluorescence in experiments.
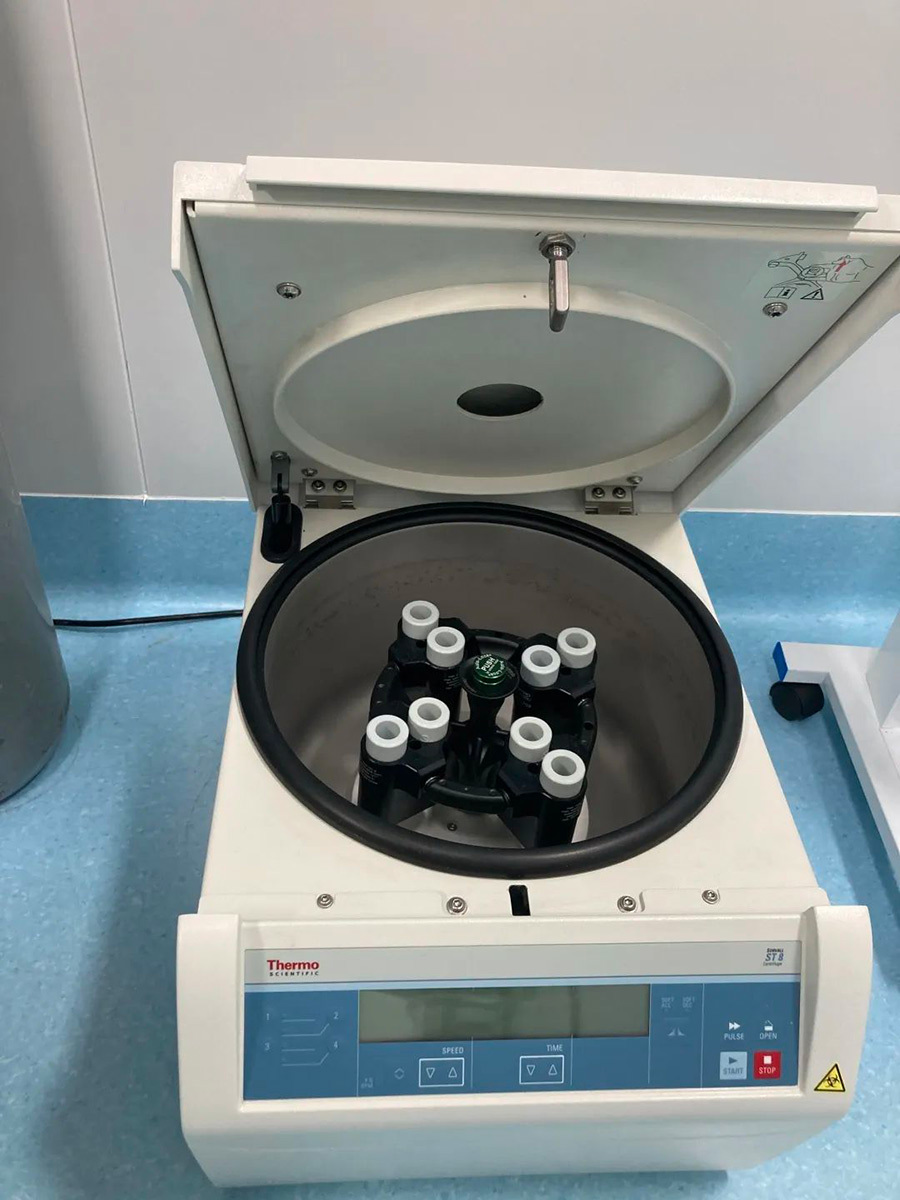

▲Centrifuge (copyrighted image, please do not reproduce)
Centrifuge: Used to separate the cells from the liquid, settle to the bottom of the centrifuge tube and collect the cells for subsequent culture or experiments, generally use 100-200g centrifugation for 3-5 minutes to separate the cells.
Commonly used culture vessels:
▲Petri dish (copyrighted image, please do not reproduce)
Petri dish: It is a flat disc shape, made of plastic and glass, it is a regular cell culture container, the specification is distinguished by the diameter of the disc, there are 35mm, 60mm, 100mm, 150mm and other specifications.

▲Petri dish (copyrighted image, please do not reproduce)
Culture flasks: bottle-shaped, the material is generally plastic, but also conventional cell culture containers, the specifications are differentiated by the bottom area (mm2), there are T25, T75, T150, T175 and so on.

▲Petri dish (copyrighted image, please do not reproduce)
Culture plate: plate-like, with small holes distributed on it, generally used for experiments, according to the number of holes is divided into 6-hole plate, 12-hole plate, 24-hole plate, 48-hole plate, 96-hole plate and so on.
02 cell recovery
Cells are stored at a very low temperature for a long period of time, usually in an ultra-low temperature refrigerator or a liquid nitrogen box. When cell experiments are required, the process of thawing the cells is known as cell recovery.
The basic principle of cell resuscitation is fast thawing, which can ensure that the extracellular crystals are melted in a very short period of time, avoiding damage to the cells due to slow thawing that causes water to penetrate into the cells to form intracellular recrystallisation.
Operation method:
①Preheat the water bath to 37℃;
② Put the cell cryopreservation tube into the water bath and shake vigorously until it just melts;
③Transfer the cell suspension to a centrifuge tube, add complete medium and centrifuge;
③Transfer the cell suspension to a centrifuge tube, add complete medium and centrifuge; ④Discard the supernatant, resuspend the cells with fresh complete medium and inoculate into the culture vessel.
Note: When resuscitating, the action should be rapid to minimise the formation of ice crystals, so as not to reduce the cell viability after resuscitation. If more cells need to be resuscitated at one time, thawing can be done in batches, and the resuscitation time is preferred to 1 minute for thawing to be completed, and should not be more than 2 minutes.
03 Cell Digestion and Transfection
When the adherent cells grow to the full extent of the culture vessel, they will not be able to continue to grow, and the cell activity will be inhibited, so it is necessary to carry out a digestion and passaging operation before they grow to the full extent, usually using trypsin digestion, trypsin can be hydrolysed and digested by the cell adherent junction protein, so that the cells are detached from the wall. Suspension cells, because they are not attached to the wall, can be directly divided into flasks and passaged.
Operation method:
①Wash the cells 2 times using PBS;
② Add trypsin and incubate at 37℃ for a certain time;
③After the cells shrink into a round shape or fall off in pieces, add complete medium to terminate the digestion, blow down the cells and transfer them to the centrifuge tube;
After centrifugation, discard the supernatant, resuspend the cells with fresh complete medium, and inoculate the cells into culture vessels.
Note: The cell digestion time should be adjusted according to the characteristics of different cells, the digestion time should not be too long, too long digestion will cause greater damage to the cells, reduce the survival rate, affect the cell morphology, and at the same time should not be in the case of insufficient digestion to force the cells to be blown down, which will also cause damage to the cells.
04 cell freezing
When the cells are not used for a short period of time, the cells can be frozen at low temperatures, which will reduce the metabolic level of the cells to extremely low levels without the need to add nutrients. However, cell freezing is not simply direct freezing of the cells, as the water inside the cells will form crystals that will puncture the cells and thus cause death, and the addition of the protective agent DMSO is required to allow the levels inside the cells to prematurely permeate the outside of the cells.
Operation method:
①Configure the cell freezing solution, the ratio is medium:serum:DMSO=7:2:1, precious cells can be configured according to serum:DMSO=9:1;
② Select cells in logarithmic growth phase, digest and centrifuge;
③ Discard the supernatant, resuspend using cell cryopreservation solution, and dispense into cell cryopreservation tubes with a cell density of 1×106 cells/mL to 1×107 cells/mL;
④ Use a programmed cooling instrument or programmed cooling box to slowly reduce the cells to a low temperature and place them in a -80℃ refrigerator or liquid nitrogen box for long-term storage.
05 Case Studies
Huaren Medical provides professional cell culture service, the research team has conducted hundreds of cell lines and primary cell culture, can be adjusted according to the cell characteristics to get the best culture method, at the same time, we can provide customised service for special cell lines, including CRISPR knockout cell lines, drug-resistant cell lines, stable overexpression cell lines and so on.
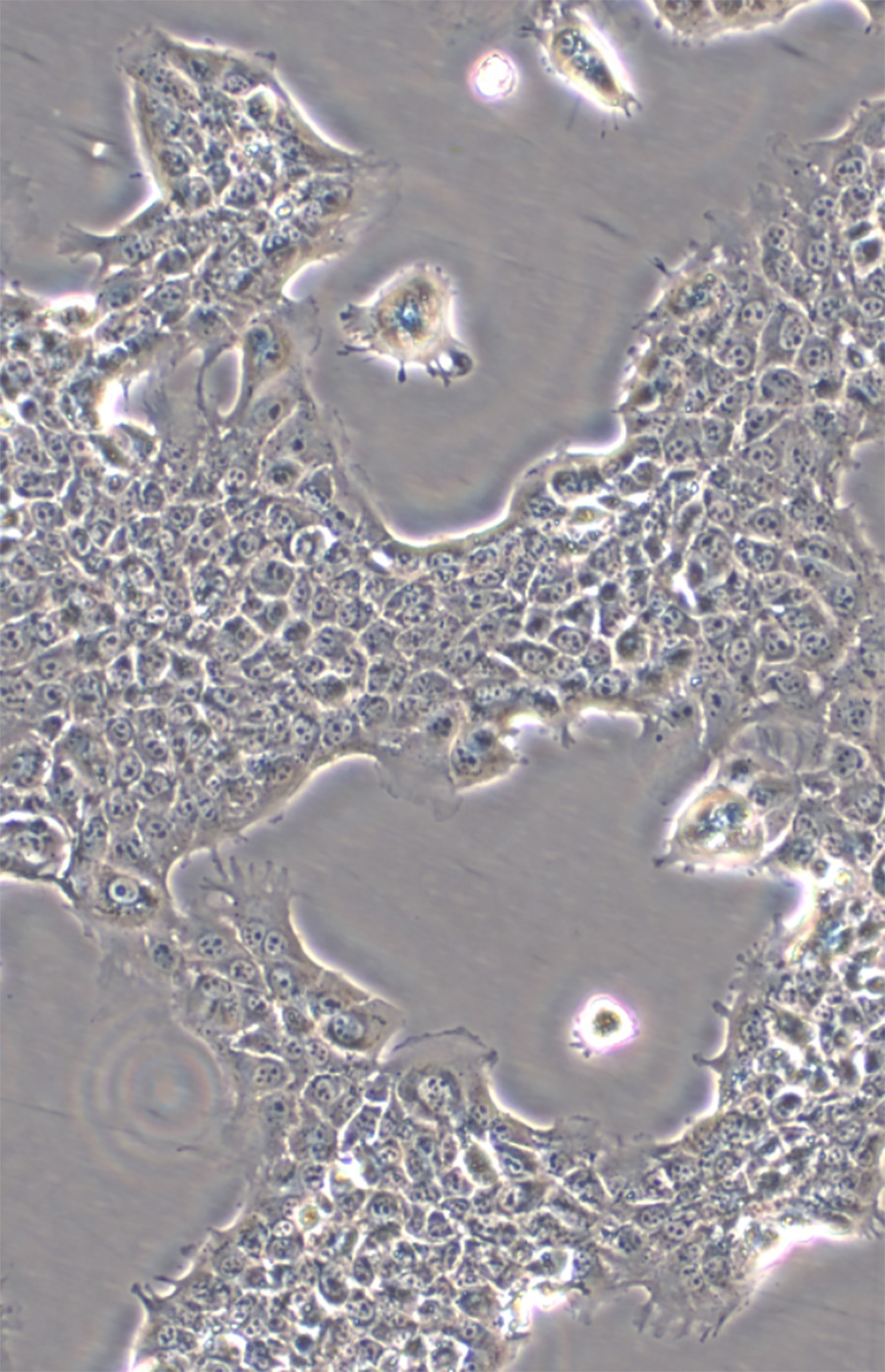
▲cytogram
· end ·


