HUAREN MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY
R & D SERVICES
Preclinical CRO
- R&D Pipeline
- Gene Therapy
Pharma CRDMO
( Contract research, development and production )
Preclinical Animal Testing

Virtual Screening
Virtual screening is a computer-simulation based technique that is primarily used to search a database of small molecule compounds to determine which are most likely to bind to and function with a drug target. Compared with traditional experimental high-throughput screening (HTS), virtual screening is a more direct and rational approach to drug discovery, with the advantages of low cost and effective screening.
During the development of drug molecules, virtual screening technology allows the screening of a large database of compounds, providing a rapid and cost-effective research method for the discovery of new active compounds. This is an important method to obtain effective active molecules for micro and small companies that are unable to perform high-throughput screening experiments. Currently, the optimization and improvement of high-throughput virtual screening methods have led to a significant increase in the hit rate of screening. Specifically, the hit rate of traditional experimental high-throughput screening is about 0.01%-0.14%, while the hit rate of purposeful virtual screening can reach 1%-40%.
|
Molecules for virtual screening |
Target of action |
Company |
|
Dorzolamid |
Carbonic anhydrase |
Merck Sharp & Dohme (pharmaceutical company) |
|
Relenza |
Neuraminidase (the N of virus such as bird flu H5N1) |
Biota |
|
Ro466240 |
Thrombin |
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd |
|
Saquinavir |
HIV protease |
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd |
|
Ag85, AG337, AG331 |
Thymidylate synthase |
Agouron |
|
Gleveca |
PTK |
Novartis AG |
|
With profound experience in molecular simulation technology, a team of professional technicians and a complete database of compounds, Huaren Medical Technology can provide users with virtual screening services based on targets or small molecules, and then select compound molecules that may have potential activity in experiments.
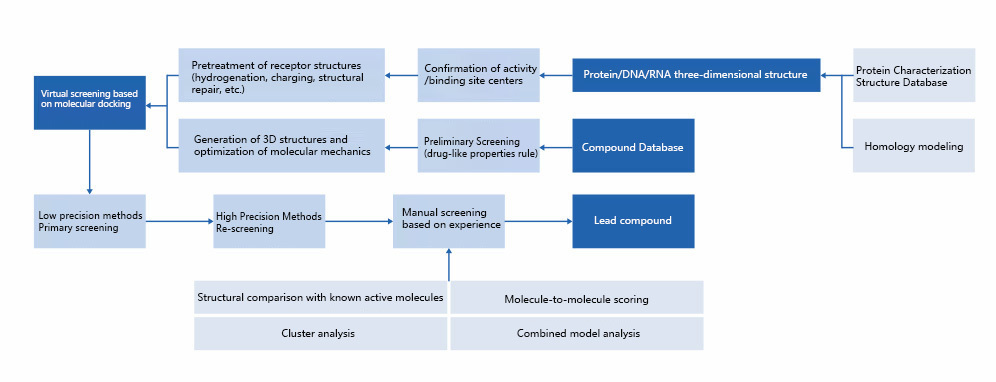
Molecular docking is one of the most important methods in structural biology and computer-aided drug design, which aims to predict the binding mode and affinity magnitude between drug targets and small molecule compounds. The main idea of molecular docking is to make small molecule compounds bind to the active site of the target by optimizing the parameters such as the space of the binding site, the hydrophobic interaction and the electrostatic interaction, etc., and to calculate the affinity magnitude between the small molecule and the target by the scoring function of molecular docking.
Molecular docking can be used in drug design to screen a large database of compounds, rank the screening results based on a scoring function, and explain the mechanism of how compound molecules inhibit/activate drug targets, which plays a very important role in the optimization of lead compounds for drug design. Currently, the molecular docking-based virtual screening (DBVS) method has become an essential tool for drug design and development, and the application of DBVS method can rapidly discover active compound molecules with novel structures.
The virtual screening method mainly consists of the following steps: 1) similarity screening of drugs; 2) virtual screening based on molecular docking; and 3) manual screening by experienced technicians. This can greatly increase the chances of obtaining active compounds by virtual screening.
Manual screening is based on the scoring function, combining the compound's binding site with the target, interaction mode, and conformational relationship with the existing active molecules, and selecting compounds with higher affinity as candidates. In the process of manual screening, interactions between compounds and important or conserved amino acids are ensured as much as possible, and more core structures of compounds are expanded as candidates, and finally the top-ranked compounds are selected for activity testing.
|