HUAREN MEDICAL TECHNOLOGY
NEWS
Scientific Information
31
2023-05
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and clinical therapy
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (HUC-MSCs) are a kind of pluripotent stem cells present in the umbilical cord tissue of newborn babies, which have strong proliferation and self-renewal ability and can be differentiated into one or more kinds of human tissues or organs under certain conditions. Through autologous/allogeneic transplantation, the structure and function of tissues and organs can be reconstructed, and immune rejection can be avoided. It is because of these immunological properties of HUC-MSCs that they have broad clinical application prospects in autoimmune diseases and various alternative therapies. In recent years, HUC-MSCs have been widely used by the medical community in the treatment of various diseases, resulting in many successful cases.
View More11
2023-05
Summary and comparison of exosome isolation methods
Exosomes are discoidal vesicles containing a variety of biomolecules, such as lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, with diameters of 30∼150 nm, which can be secreted by all cell types, and are found in plasma, urine, semen, saliva, bronchial fluids, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), breast milk, serum, amniotic fluid, synovial fluids, lacrimal fluids, lymphatic fluids, bile, and gastric acids [1].
View More25
2023-04
Criteria for assessing the effects of anaesthesia in experimental animals
Anaesthesia, as a method of animal preservation, is widely used in the study of clinical diagnosis and treatment of animals, animal experiments, and wildlife capture [1]. Scientific research on healthy animals and the establishment of necessary animal models are important tools for studying human diseases and ensuring human health [2]. The experimental research on animals often requires chemical preservation (anaesthesia), but it is more difficult to assess the depth of anaesthesia when performing animal anaesthesia, this paper assesses and judges the sedation, anaesthesia effect and anaesthesia resuscitation degree by the changes in respiratory rate, heart rate, blood pressure, eyeballs, pupils, chromatophore reflexes, lip colour, muscle tension, skin colour, limb mobility, etc., in the experimental animals.
View More23
2023-04
What do you know about blood collection in laboratory animals
In experimental animal research, blood is often collected from experimental animals for testing and analysis. Researchers need to know the amount of blood circulating in the animals, which depends on the species, sex, age, health and nutritional status. For the same species, larger animals have less circulating blood volume than smaller animals, and older and obese animals have less circulating blood volume than younger and normal weight animals. Table 1 shows the circulating blood volume of common laboratory animals.
View More18
2023-04
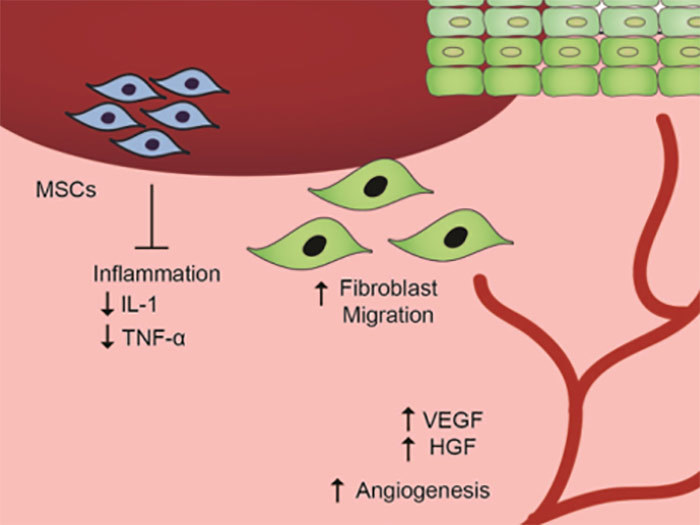
Stem cells in chronic wound healing
Trauma, burns and many chronic diseases, such as diabetes and peripheral vascular disease, can lead to chronic intractable wounds. As the prevalence of obesity and diabetes rises, so does the incidence of chronic wounds. Such wounds pose a great challenge for clinical management and have a serious impact on the patient's image and psychology. Currently, treatments for chronic wounds include debridement, topical antibiotics, compression bandages, skin grafts, and growth factors. However, the results are unsatisfactory and there is an urgent need to explore new approaches.
View More16
2023-04
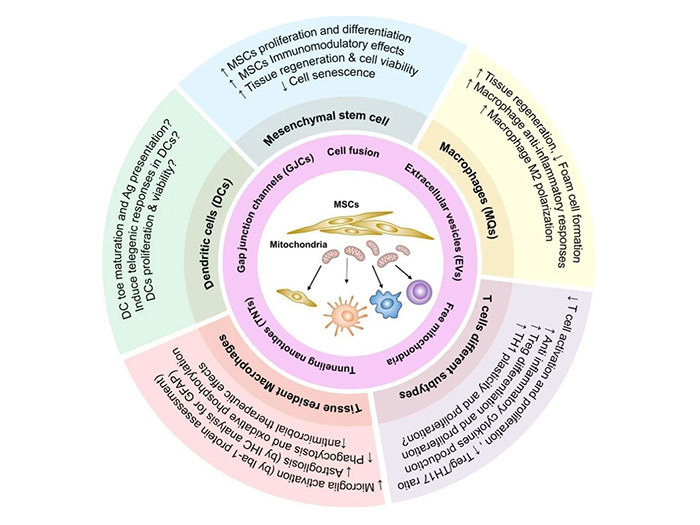
A new mechanism of action for mesenchymal stem cells - mitochondrial therapy
MSCs are one of the most commonly used candidate cells in regenerative medicine research and show great potential in clinical therapy, improving tissue function and treating various diseases through mechanisms of action such as secretion of factors, transfer of extracellular vesicles, migration to the site of injury, differentiation into different cells, and restoration of cell function [1]. The cellular state of pathological environments in clinical settings can be affected, causing damage to cellular mitochondria, leading to a decrease in ATP production and triggering impaired cellular function or even death. Recently, a new strategy called mitochondrial therapy is being investigated for different diseases, based on the principle of using exogenous mitochondria to transfer into cells and thus repair the pathological state. MSCs, a pioneer in the field of cellular therapy, can serve as a good donor for the transfer of functional mitochondria into damaged cells (Figure 1) [2]. Studies have shown that mitochondrial transfer of MSCs can affect other cells in important processes such as proliferation, differentiation, metabolism, inflammatory response, senescence, stress and migration [3].
View More